Chapter 2
Australia's energy consumption, production, imports and exports
2.1
This chapter provides an overview of Australia's energy consumption,
imports and exports, as well as energy production and storage capacity.
Australia's energy consumption
2.2
According to the Bureau of Resources and Energy Economics (BREE),
Australia's energy consumption has consistently risen over the past ten years
at an average annual rate of 1.1 per cent.[1]
2.3
Fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas) dominate Australia's primary energy
consumption.[2]
In 2012–13, of the 5885 petajoules of energy consumed in Australia, 94 per cent
was derived from fossil fuel sources.[3]
2.4
In 2012–13, of Australia's total energy consumption, approximately:
-
38 per cent comprised oil – including crude, condensate and liquefied
petroleum gas (LPG);
-
33 comprised coal – both black and brown;
-
24 per cent comprised natural gas; and
-
6 per cent was made up in renewable resources – wind, solar,
geothermal, hydro, wave, tidal and bioenergy.[4]
Energy consumption within the transport sector
2.5
Australia's demand for oil has risen steadily over recent decades,
largely driven by increasing transport sector demand.[5]
2.6
In 2012–13, the transport sector was Australia's second largest energy
consumer (behind the electricity sector), accounting for 26 per cent of all
energy consumption or 1545 petajoules of energy.[6]
Increased energy use in road, rail and air transport resulted in a marginal
increase in energy consumption in the transport sector from the previous year.[7]
The agricultural sector accounted for 1.7 per cent or 99 petajoules of total
energy consumption.[8]
2.7
The Australian economy is dependent on extensive transport networks to
move people, goods and resources domestically and offshore. Conventional transport
fuels such as petrol, diesel and jet fuel are derived from crude oil and
comprise the largest component of fuel sales in Australia.[9]
Evidence to the committee highlighted that the country's transport sector is
almost totally reliant on refined liquid fuels (oil, refined petroleum products
and gaseous transport fuels).[10]
The sector consumes 73 per cent of all Australia's liquid fuel supplies
(including LPG and refined products).[11]
In 2012–13, road transport accounted for 74 per cent of this.[12]
2.8
Alternative transport fuels include biofuels (ethanol and biodiesel),
gaseous fuels and synthetic fuels.[13]
In 2011–12, over 95 per cent of energy used for all transport modes was crude
oil-derived liquid fuels with LPG the most significant alternative fuel comprising
2.7 per cent.[14]
Over that period, most of the 32 billion litres of petrol, diesel and LPG used
by cars, buses and trucks in Australia was imported.[15]
2.9
Evidence to the committee suggested that energy diversification has
taken place in all industries (including agriculture, industry, residential and
commercial sectors) except that of transport.[16]
While there been some uptake of electric vehicles in the light passenger sector
and some electrification in the passenger rail and bulk rail freight sectors, most
transport sectors and particularly heavy road freight, maritime and aviation
transport are likely to remain wholly or largely oil dependent for decades to
come.[17]
Therefore, as noted in the 2014 Energy White Paper Issues Paper, changes in
energy sources offer the potential to both increase the productivity of energy
use and reduce reliance on petroleum-based liquid fuels.[18]
Diagram 2.1: Energy consumption in
Australia's transport sector 2012–13 [19]
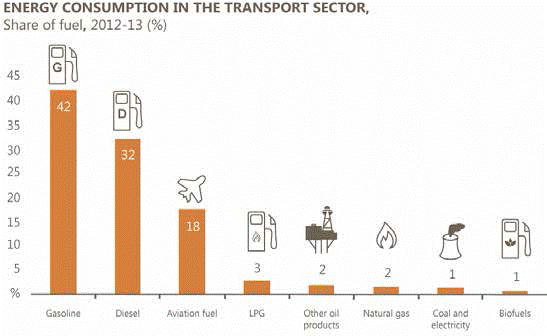
Australia's energy imports
2.10
Australia is a net importer of crude oil and refined petroleum products.
In 2013–14, 82 per cent of the crude and other feedstock required for domestic
refining was imported, with the balance supplied from indigenous production.[20]
2.11
Almost all of Australia's transport needs are met by oil-derived
products including petrol, diesel, jet fuel and LPG.[21]
An estimated 91 per cent of Australia's transport fuel (petrol and diesel) is
imported either as oil to be refined in Australia or as refined fuel products.[22]
In 2000, Australia imported 60 per cent of its transport fuel.[23]
2.12
As one of the largest consumers of liquid fuels in Australia, the Qantas
Group spent a record $4.5 billion on aviation fuel in 2013–14, despite a
reduction in fuel consumption by 5.4 per cent.[24]
2.13
In 2013–14, Australia's total petroleum imports comprised the majority
of energy imports, amounting to almost $42.8 billion, up on the previous year's
$40.15 billion.[25]
Diagram 2.2: Australian Petroleum
Statistics – Imports of petroleum by product [26]
|
Year
|
Crude oil & other refinery feedstock
|
TOTAL petroleum imports[27]
|
|
2010-11
|
31,773.9 ML
|
6,574,906.3 ML
|
|
2011-12
|
29,504.9 ML
|
5,861,947.5 ML
|
|
2012-13
|
29,519.8 ML
|
6,569,689.9 ML
|
|
2013-14
|
27,677.7 ML
|
6,990,150.4 ML
|
2.14
AGL Energy Limited stated that:
Australia's quarterly imports of fuels and lubricants reached
$10.9 billion in December 2013, more than a 300 per cent increase since 2003
and represented 13 per cent of the value of Australia's total imported goods
and services. With the projected rises in petroleum import volumes and oil
prices, the value of imported fuels could increase in real terms by over 20 per
cent by 2025 and 40 per cent by 2030.[28]
2.15
Australia's largest export markets for crude oil and other refinery
feedstock are Singapore, Thailand and Korea.[29]
Of total imports, up to 58 per cent of product supply comes from Singapore.[30]
However, Australia also imports crude oil and other refinery feedstock from a
wider range of countries including Malaysia, United Arab Emirates, Vietnam and
Nigeria while refined products are imported from countries including South
Korea, Japan and Indonesia.[31]As
a case in point, 58 per cent of crude oil imported by ExxonMobil Australia comes
from the Asia-Pacific market, 21 per cent from west Africa and approximately 13
per cent from the Middle East while 85 per cent of its finished product comes
from the Asia-Pacific region.[32]
Australia's energy production, refining and exports
2.16
Australia produces a range of liquid fuels including crude oil,
condensate and LPG. In 2013–14, approximately 75 per cent of Australia's oil
production was exported with crude oil exports alone earning an estimated $11.1
billion.[33]
2.17
The majority of Australia's crude oil production is exported because the
qualities and characteristics of Australian oil are more suited to export
markets than the Australian refinery market.[34]
For example, most of the liquid fuels production from the North West Shelf
(Western Australia) is in the form of condensates, which are not suited to the
existing infrastructure of Australian refineries.[35]
2.18
Primary energy (coal, crude oil, natural gas and wood) production in
Australia amounted to 19,318 petajoules in 2012–13. Of the total energy
produced during this period for both domestic use and export:
-
59 per cent was coal;
-
22 per cent was uranium;
-
13 per cent was natural gas;
-
5 per cent was oil and LPG; and
-
2 per cent was derived from renewable energy (primarily bioenergy
and hydro).[36]
2.19
According to the Australian Petroleum Statistics (APS), Australia's
production of crude oil and condensate declined from 25,772 megalitres (ML) in
2010–11 to 20,405 ML in 2013–14.[37]
BREE noted that this fall in output continued a long term decline in Australia's
production of primary petroleum.[38]
In this regard, Australia's production of oil and condensate is forecast to
decline from 147 million barrels in 2014 to 83 million barrels in 2030.[39]
Diagram 2.3: Australian Petroleum
Statistics – Petroleum production, Australia [40]
|
Year
|
Total crude oil & condensate
|
LPG (naturally occurring)
|
Ethane
|
Natural gas
|
|
2010-11
|
25,772 ML
|
3,906 ML
|
407 Mm³
|
47,558 Mm³
|
|
2011-12
|
24,068 ML
|
3,813 ML
|
416 Mm³
|
45,173 Mm³
|
|
2012-13
|
21,267 ML
|
3,627 ML
|
419 Mm³
|
52,299 Mm³
|
|
2013-14
|
20,405 ML
|
3,912 ML
|
445 Mm³
|
52,692 Mm³
|
2.20
Australia has significant volumes of natural gas reserves that are
increasingly being developed for domestic use and for liquefied natural gas (LNG)
exports.[41]
In 2012–13, Australia produced 2439 petajoules (or around 62 billion cubic
metres) of natural gas, representing a rise in production of 14 per cent from
the previous year.[42]
BREE noted that, over the past decade, Australia's natural gas production had
expanded by 5 per cent a year on average.[43]
2.21
Around 48 per cent of Australia's gas was produced for the domestic
market in 2013–14, with the remainder exported as LNG.[44]
According to BREE, the share of production consumed by the domestic market fell
from 71 per cent a decade ago, with exports increasing at a faster rate than
domestic consumption.[45]
As the world's third largest exporter of LNG behind Qatar and Malaysia,
Australia accounts for 10 per cent of the world LNG trade.[46]
In 2013–14, Australian LNG exports amounted to 24.1 million tonnes, an increase
from 23.9 million tonnes in 2012–13.[47]
In 2013–14, LNG exports were valued at more than $16 billion.[48]
Domestic refining
2.22
The refining industry in Australia produces a range of petroleum
products including gasoline, diesel oil, aviation turbine fuel, fuel oil and
LPG.[49]
According to BREE, in 2013–14, Australian refineries produced 34,187 ML of
marketable refined petroleum products, down from 36,891 ML in 2012–13.[50]
2.23
In 2010, total refinery intake of the then seven refineries in Australia
averaged 666,000 barrels per day (of which 605,000 barrels was crude and
condensates). According to IEA, at that time, over two-thirds (or about 66 per
cent) of Australia's refinery input requirements came from imports.[51]
This figure rose to 80 per cent in 2014 as noted by BREE:
Just over 80 per cent of the feedstock for Australia’s five
domestic refineries, which are largely based on the east coast, is sourced from
imports. Imports also account for a significant share of Australia’s
consumption of refined products. In 2013–14 imports of refined products
equalled 44 per cent of domestic consumption.[52]
2.24
The five petroleum refineries currently operating in Australia have a
combined capacity of 32.6 gigalitres a year.[53]
By mid–2015 when BP's refining operations at the Bulwer Island refinery in
Brisbane close, Australia will only have four refineries – Vitol in Geelong, BP
at Kwinana, Western Australia, Caltex in Lytton, Brisbane and ExxonMobil in
Altona, Melbourne.[54]
2.25
With the reduction in Australia's refining capacity, a larger percentage
of refined product will have to be imported.[55]
NRMA noted that between mid–2012 and mid–2015, Australia is expected to lose 40
per cent of its oil refining capacity.[56]
2.26
Since 2002, the proportion of refined petroleum, oils and lubricants
sourced from overseas rose from 11 per cent to 37 per cent in 2012 and was
expected to reach 43 per cent in 2014 with the closure and conversion of the
NSW refineries.[57]
Evidence to the committee suggested that without discovery and
commercialisation of substantial new oil reserves, this supply-demand imbalance
will become more pronounced. In fact, projections suggest that by 2035,
Australian production will be equivalent to only 12 per cent of consumption.[58]
Australia's storage capacity
2.27
All storage capacity in Australia is held commercially within the supply
chain, with no capacity for emergency reserves in the form of government-held
or compulsory industry stocks.[59]
2.28
In response to Australia's growing dependence on imported oil, petroleum
companies have responded by converting existing oil refineries into fuel
storage facilities for finished fuel products sourced from international
refineries. The conversion of the Caltex Kurnell refinery was the most recent
of these conversions.[60]
AIP made the point that the conversion of refineries to import terminals led to
a substantial increase in the availability of finished product tankage.[61]
Similarly, the Department of Industry and Science (department) noted that:
While product imports are increasing, crude oil imports are
decreasing, gross import dependency remains similar. Each refinery closure has
been accompanied by conversion of these facilities to product import terminals
to provide the necessary infrastructure for maintaining domestic supply.[62]
2.29
A 2009 study by ACIL Tasman commissioned by the then Department of
Resources, Energy and Tourism estimated that the storage capacity of the main
storage facilities across Australia was just over 42 million barrels (6.7
million cubic metres). This figure did not, however, take into account all
storage capacity across the country as information from smaller industry
participants and independent importers was not included in the study.[63]
2.30
The central argument of many submitters to this inquiry was that
Australia's growing inability to comply with the IEA 90 day requirements is a
consequence of a progressive decline in Australia's oil production coupled with
growing oil demand. They argued the point that this decline and corresponding
dependence on oil imports exposes Australia's fuel supply to considerable risk
of interruption and insecurity. The following chapter explores the evidence
regarding Australia's supply security.
Navigation: Previous Page | Contents | Next Page